CHC Group pays close attention to changes in the water environment. When utilizing water resources, we comprehensively consider relevant policies and regulations, environmental risks, and business needs, striving for effective scheduling and reasonable allocation. In addition, through the use of water-saving equipment, water supply regulation, reclaimed water recovery and reuse, and water conservation actions, we continue to enhance the efficiency of water resource utilization. In order to strengthen water resource management, the Group keeps records of water usage behavior, types of water sources, water consumption, and water discharge at each site. The water supply for the Group’s office locations and construction areas is provided by the Taiwan Water Corporation.
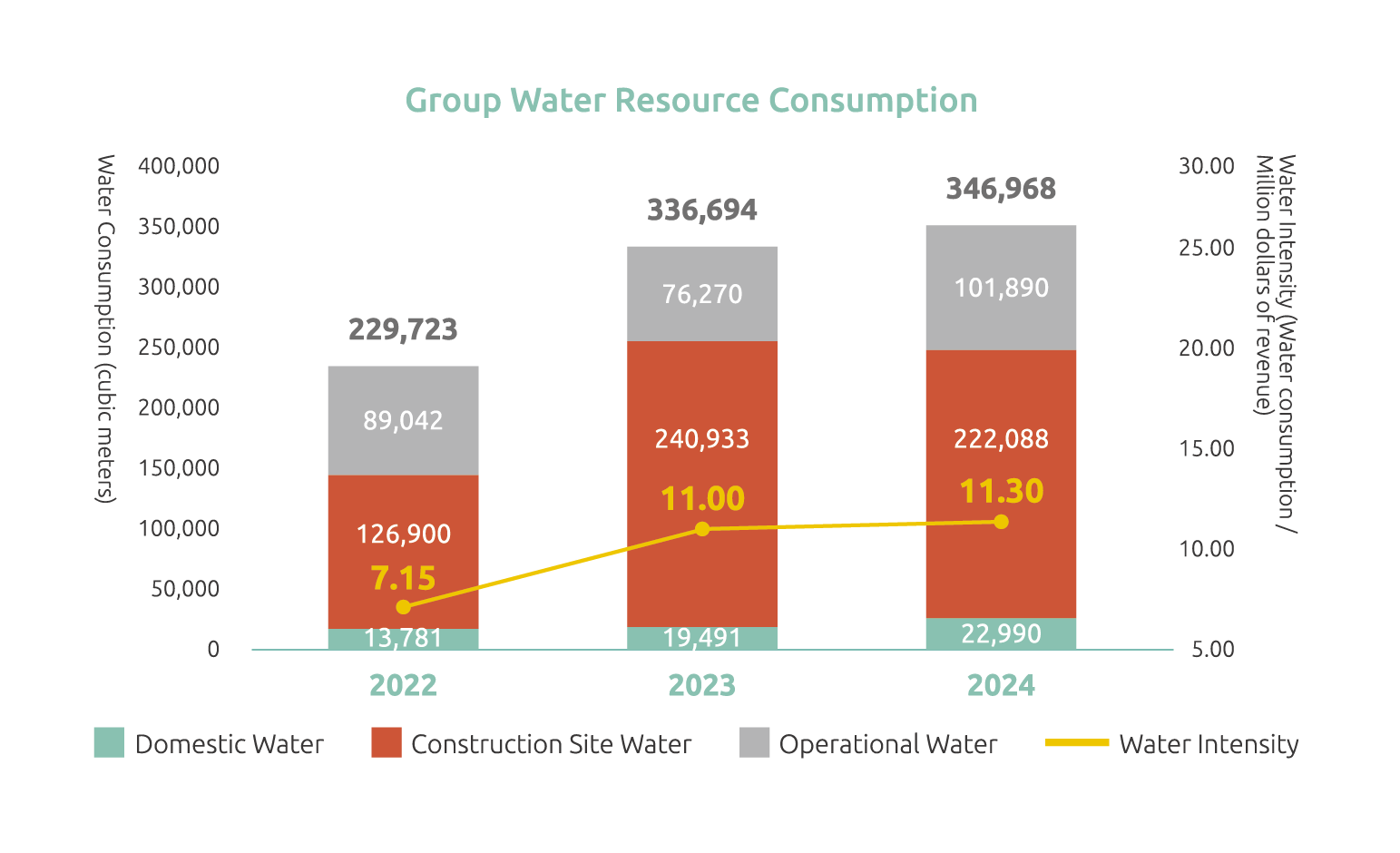
Note: The inventory boundary 2022 to 2024 includes the Group’s headquarters building, CEC’s construction sites, HDEC’s operational bases and construction sites.
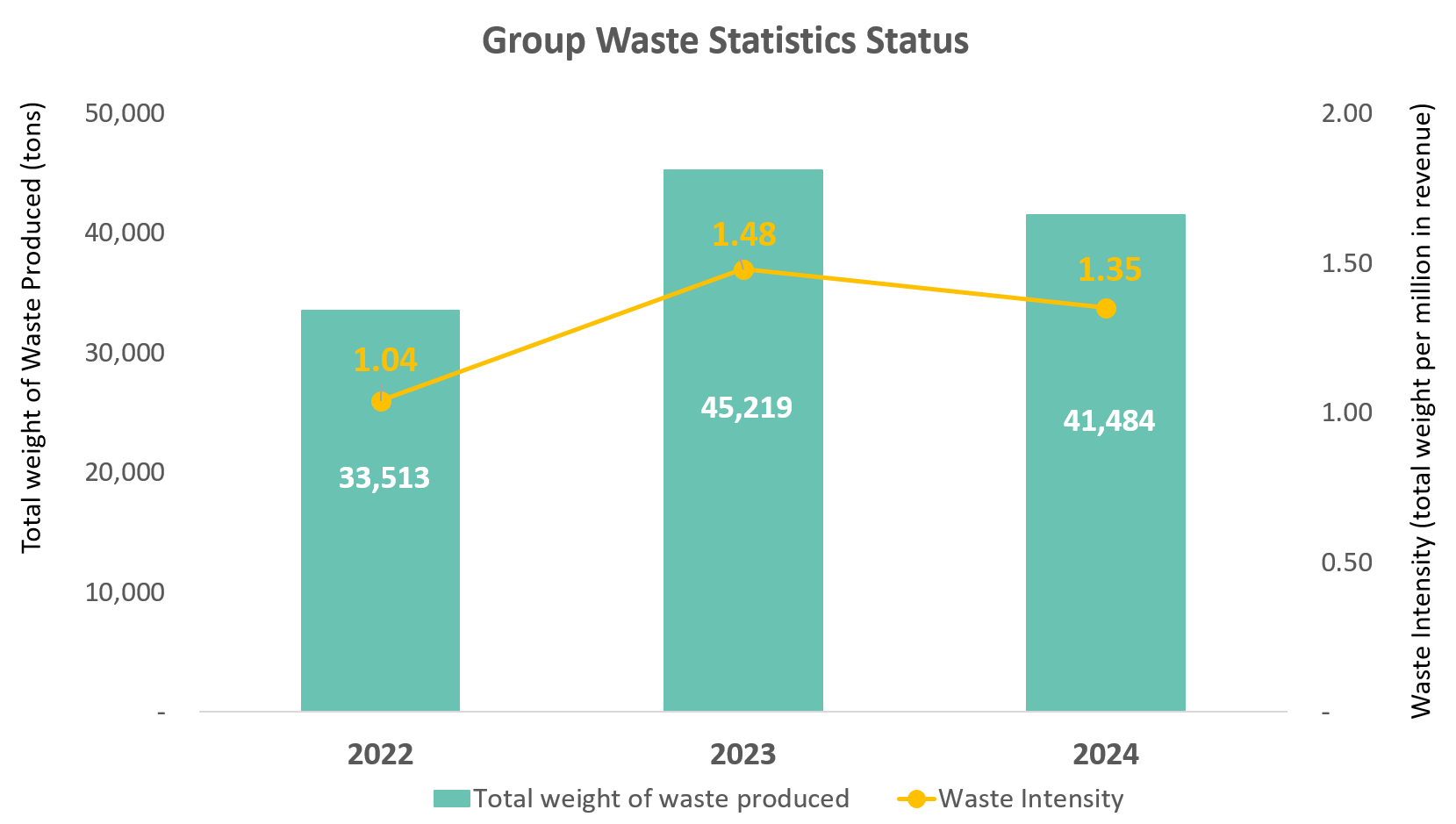
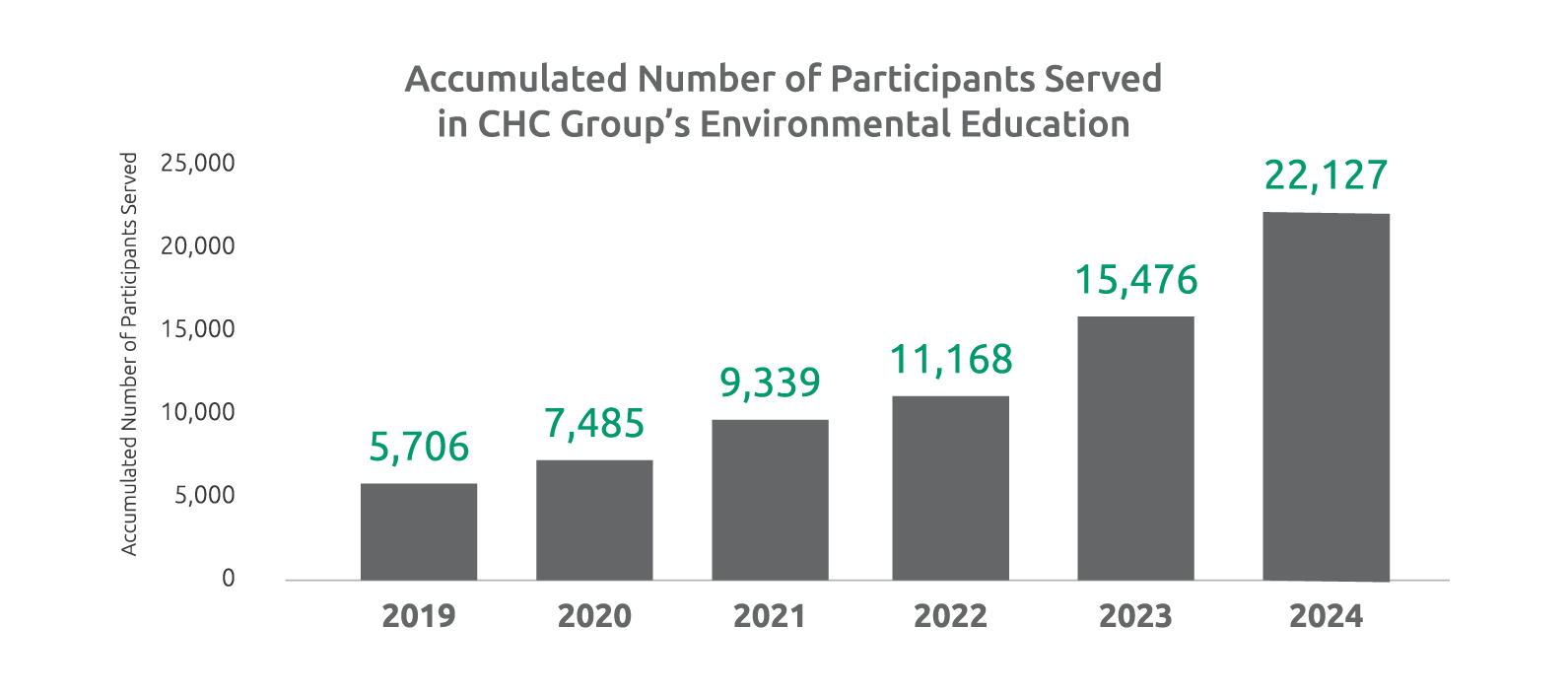
In 2024, the Group’s total water consumption amounted to 346,968 cubic meters, with a water intensity of 11.30 cubic meters per million NTD in revenue. Approximately 60% was used for construction, while water treatment operations accounted for 29%.
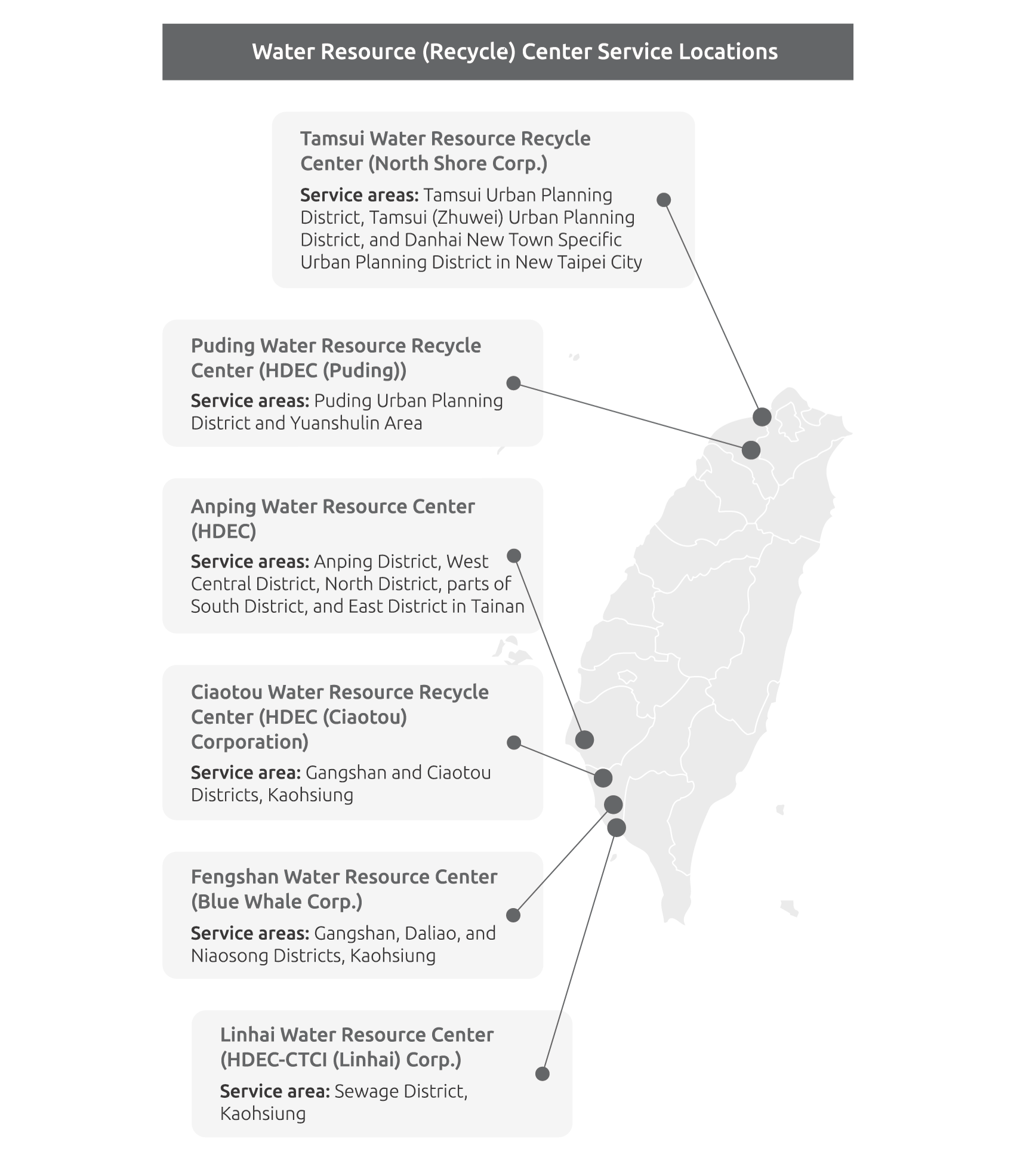
CHC Group actively implements water resource recycling and reuse, applying reclaimed water to operational equipment use and cleaning, inflow water for reclaimed water treatment, water for wastewater treatment pools, environmental cleaning, wetland replenishment, and roadside tree irrigation, among other purposes. These measures not only reduce the Group’s own water consumption but also provide water for external uses such as washing, street cleaning or irrigating roadside trees. In 2024, all water resource centers of the Group, except for Anping and Linhai Water Resource Centers, achieved their targets for reclaimed water reuse, totaling 73,010,838 metric tons of reclaimed water. The reclaimed water rate reached 64%, an increase of about 10% from 2023, effectively enhancing water resource utilization efficiency.
In addition, the Group’s water conservation actions focus on both “source expansion” and “water saving.” The former includes the reuse of water from well points and the harvesting and utilization of rainwater; the latter encompasses the installation of water-saving devices and equipment, water conservation management, and adjustments to the water supply system. In 2024, the Group’s measurable water-saving actions resulted in a total reduction of 19,850 metric tons of water consumption.